VBN, which stands for Virtual Backbone Network, is an advanced networking concept that enhances the capabilities of proxy servers. It is designed to provide a more efficient, secure, and reliable way of handling data traffic within a network, especially when dealing with large-scale internet operations. VBN operates as an overlay network, built on top of the existing infrastructure, to optimize data transmission, improve network performance, and strengthen overall security.
The history of the origin of VBN and the first mention of it.
The concept of Virtual Backbone Network (VBN) traces its origins to the early 2000s when researchers were seeking solutions to tackle the increasing complexity of internet traffic routing. The term “Virtual Backbone Network” was first mentioned in academic papers and technical discussions during this period, where it was identified as a method to alleviate congestion and enhance data delivery across interconnected networks.
Detailed information about VBN. Expanding the topic VBN.
A Virtual Backbone Network is primarily designed to address the following challenges faced by traditional networks:
- Traffic Optimization: VBN efficiently routes data packets between various nodes within a network, optimizing the data paths for faster transmission and reduced latency.
- Scalability: As networks grow in size and complexity, VBN allows for seamless scalability, ensuring the network can handle increased data traffic without compromising performance.
- Reliability: By dynamically adapting to changes in network topology and traffic patterns, VBN ensures high reliability, even in the face of network failures or disruptions.
- Security Enhancement: VBN enhances security by providing encrypted data tunnels, making it harder for unauthorized parties to intercept sensitive information.
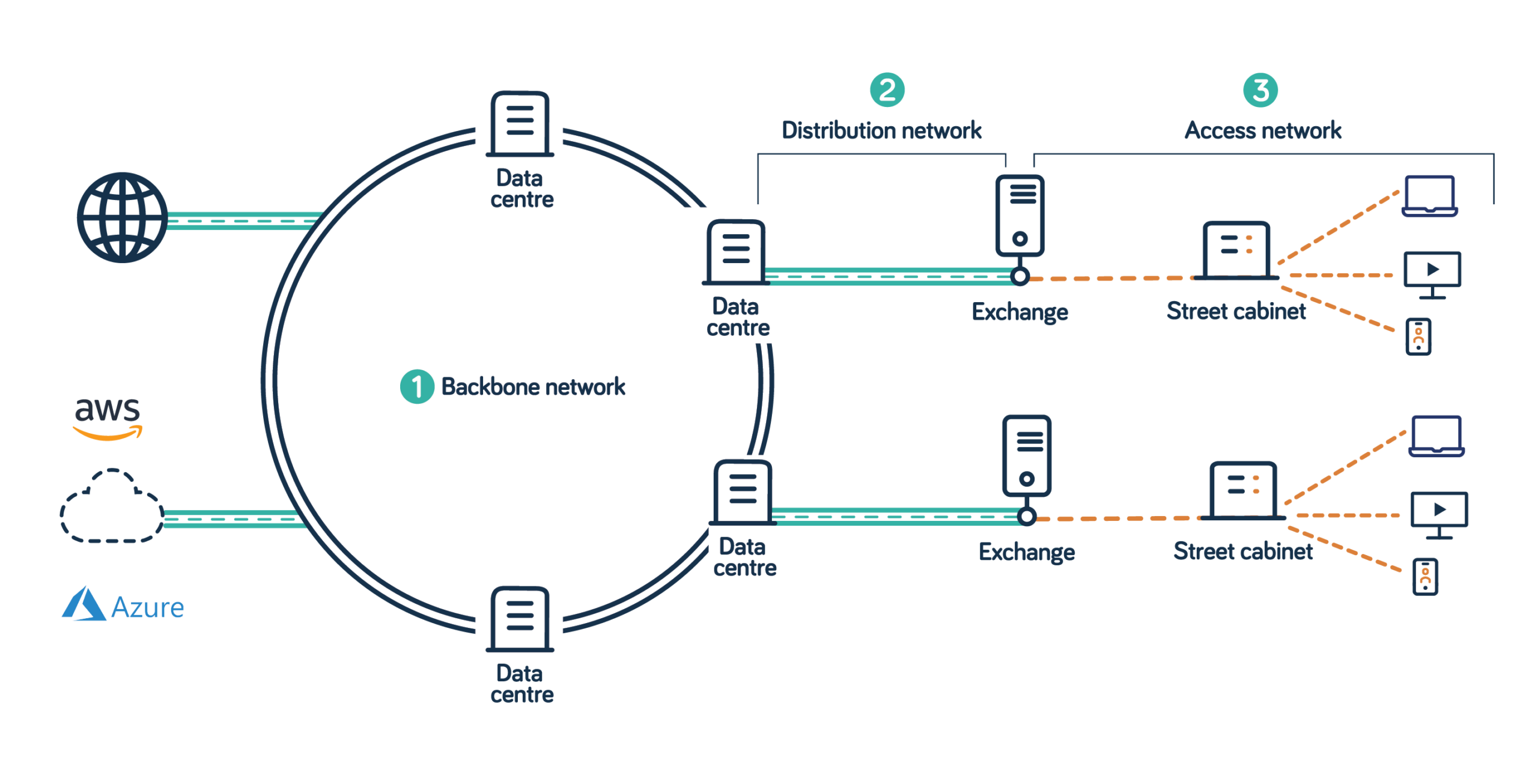
The internal structure of the VBN. How the VBN works.
The internal structure of a Virtual Backbone Network involves three fundamental components:
- Virtual Nodes: These are logical points within the VBN that act as intermediaries between the source and destination of data traffic. Virtual nodes dynamically analyze the best path for data transmission, considering factors like congestion, latency, and reliability.
- Virtual Links: Virtual links establish connections between virtual nodes, forming the data transmission paths within the VBN. These links are optimized based on real-time network conditions to ensure efficient data delivery.
- Routing Algorithm: The core of VBN’s functionality lies in its routing algorithm, which determines the most suitable path for data packets to traverse through the network. The routing algorithm continuously adapts to network changes, ensuring optimal performance.
Analysis of the key features of VBN.
The key features of Virtual Backbone Networks include:
- Traffic Load Balancing: VBN intelligently distributes data traffic across multiple paths, preventing congestion and ensuring an even load distribution.
- Fault Tolerance: The dynamic nature of VBN enables it to reroute traffic around network failures, providing fault tolerance and uninterrupted service.
- QoS (Quality of Service) Improvement: VBN can prioritize critical data traffic, ensuring high-quality service for essential applications and services.
- Reduced Latency: By optimizing data paths, VBN significantly reduces latency, leading to improved overall network performance.
Types of VBN
Virtual Backbone Networks can be categorized based on their scope and application:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Local VBN | Operates within a localized area, such as a data center, optimizing traffic flow within that environment. |
| Global VBN | Spans across multiple geographically distributed locations, enabling efficient data transmission across vast distances. |
| Provider-managed VBN | Offered as a service by network providers, allowing organizations to outsource the management and optimization of their network’s backbone to experts. |
| DIY VBN | Allows organizations to create and manage their Virtual Backbone Network using specialized software and hardware tailored to their unique needs. |
Ways to use VBN:
- Enterprise Networking: Organizations can deploy VBNs to enhance internal data communication, improve interdepartmental connectivity, and boost overall productivity.
- Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): CDNs can employ VBNs to optimize the delivery of content to end-users, reducing latency and improving user experience.
- Cloud Services: Cloud providers can leverage VBNs to optimize data traffic between their data centers, ensuring seamless service delivery.
Problems and Solutions:
- Complex Configuration: Setting up a VBN can be challenging. To address this, managed VBN services offer expert configuration and maintenance.
- Compatibility: Ensuring compatibility with existing network infrastructures can be a concern. Providers should offer customized solutions tailored to each client’s network.
- Security Risks: While VBNs enhance security, they can still be vulnerable to attacks. Regular security audits and updates are essential to mitigate risks.
Main characteristics and other comparisons with similar terms in the form of tables and lists.
| Characteristic | Virtual Backbone Network (VBN) | Virtual Private Network (VPN) | Content Delivery Network (CDN) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Function | Optimize data traffic, enhance network performance, and improve security. | Securely extend a private network over a public network (Internet). | Efficiently deliver content to end-users, reducing latency and server load. |
| Scope | Can be local or global, depending on the deployment. | Primarily used to establish secure connections for remote access. | Global networks of distributed servers and data centers. |
| Primary Use Cases | Enterprise networking, cloud services optimization. | Remote work, secure data transfer between offices. | Content caching, media streaming, website acceleration. |
| Security | Enhances security through encrypted data tunnels and optimized routing. | Encrypts data to secure communication channels. | Ensures data integrity and protects against DDoS attacks. |
| Routing Mechanism | Dynamic routing algorithm based on real-time network conditions. | Static and dynamic routing protocols. | Anycast routing for optimal content delivery. |
The future of Virtual Backbone Networks holds promising advancements and potential applications:
- AI-Driven Routing: Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into VBN routing algorithms will enable even more efficient and adaptive data path optimization.
- Edge Computing Integration: VBNs can be integrated with edge computing infrastructure, reducing data transit times and enhancing the performance of edge devices.
- 5G and VBN Synergy: The emergence of 5G technology will complement VBNs by providing faster and more reliable connections, further enhancing network performance.
How proxy servers can be used or associated with VBN.
Proxy servers play a complementary role in the functioning of Virtual Backbone Networks:
- Enhanced Anonymity: Proxy servers can be used within the VBN to further anonymize users’ internet activities, ensuring privacy and security.
- Load Balancing: Proxy servers can distribute traffic across multiple VBN entry points, helping to balance the load and improve overall network performance.
- Geo-Redundancy: By utilizing proxy servers in different geographical locations, VBNs can achieve geo-redundancy, enhancing fault tolerance and reliability.
Related links
For more information about Virtual Backbone Networks (VBN) and related technologies, you can explore the following links:
- Distributed construction of virtual backbone network (VBN) for battlefield data link with alien platform
- What Is A Backbone Network?
- Exploring Backbone Networks: Understanding Distribution and Core Layers
- Connecting LANs, Backbone Networks, and Virtual LANs
In conclusion, Virtual Backbone Networks (VBN) offer a robust solution to the challenges faced by traditional networks. By optimizing data traffic, enhancing security, and improving overall network performance, VBNs pave the way for a more efficient and reliable internet experience. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see further advancements and innovations that will solidify the role of VBNs in shaping the future of networking.




