GhostNet is an enigmatic and controversial term that refers to a sophisticated network used for covert surveillance and cyber-espionage. Its existence was first publicly revealed in reports published by two Canadian research groups, the Information Warfare Monitor and the Shadowserver Foundation, back in 2009. The network came into the spotlight due to its involvement in targeting various governmental and political entities worldwide.
The History of the Origin of GhostNet and Its First Mention
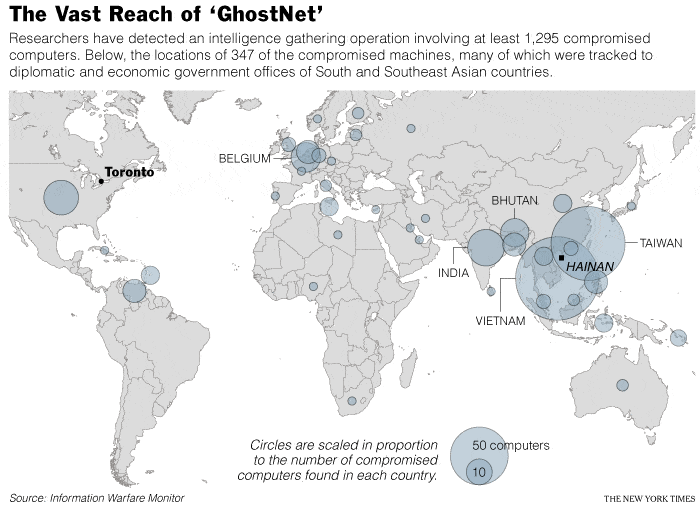
The origin of GhostNet remains shrouded in mystery, with no definitive attribution to a particular entity. In March 2009, when the Information Warfare Monitor and the Shadowserver Foundation released their report titled “Tracking GhostNet: Investigating a Cyber Espionage Network,” it marked the first time the network was brought to public attention. According to the report, GhostNet had infiltrated sensitive computer networks in over 100 countries, with a strong focus on targets in Asia.
Detailed Information about GhostNet: Expanding the Topic
GhostNet is not a single piece of software or a specific tool; rather, it is a complex network of compromised computers (bots) that are controlled by a central command and control (C&C) infrastructure. The attackers use sophisticated social engineering techniques and malicious software, such as Trojans and keyloggers, to gain unauthorized access to target systems. Once a computer is compromised, it becomes part of the GhostNet botnet, allowing the attackers to remotely control it.
The Internal Structure of GhostNet: How It Works
At its core, GhostNet relies on a hierarchical structure with a central command center overseeing various regional and local nodes. This design allows the operators to efficiently manage and coordinate the activities of the infected computers. The compromised systems act as relay points, ensuring the anonymity of the attackers and enabling them to communicate with the infected bots without revealing their true identities.
Analysis of the Key Features of GhostNet
The key features that distinguish GhostNet from conventional malware or cyber-espionage campaigns are:
- Stealthy Operation: GhostNet operates covertly, avoiding detection and raising minimal suspicion while infiltrating its targets.
- Surgical Targeting: The network exhibits a surgical approach, focusing on high-value targets such as government agencies, diplomatic institutions, and political organizations.
- Global Reach: GhostNet’s vast geographical reach spanning over 100 countries showcases its global scale and impact.
- Persistent Threat: The network’s ability to maintain persistence on infected systems ensures prolonged access for data exfiltration and intelligence gathering.
Types of GhostNet Existence
GhostNet, being a generic term for a specific type of cyber-espionage network, can manifest in various forms based on its objectives, targets, and origins. Below are some common types of GhostNet networks:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Governmental GhostNet | Networks targeting government and diplomatic entities for intelligence. |
| Political GhostNet | Networks focused on political organizations, aiming to influence agendas. |
| Corporate GhostNet | Espionage networks seeking sensitive corporate information for advantage. |
Ways to Use GhostNet, Problems, and Solutions
Ways to Use GhostNet
GhostNet is primarily employed for:
- Espionage and Surveillance: Gathering sensitive information from target systems and organizations.
- Influence Operations: Attempting to sway political or public opinion through targeted information leaks.
- Intellectual Property Theft: Stealing trade secrets and proprietary information to gain a competitive edge.
Problems and Solutions Related to the Use
GhostNet poses significant security and privacy concerns, especially for governments and organizations. The main problems include:
- Data Breaches: Compromised systems lead to potential data breaches and privacy violations.
- National Security Threat: Targeting governmental entities can undermine national security.
- Economic Impact: Corporate espionage can cause financial losses and damage economies.
To mitigate these problems, organizations and individuals should adopt robust cybersecurity practices, including:
- Regular software updates and patches to protect against known vulnerabilities.
- Strong password policies and multi-factor authentication to prevent unauthorized access.
- Implementing firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and antivirus software to detect and block malicious activities.
Main Characteristics and Comparisons with Similar Terms
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| GhostNet | A cyber-espionage network using botnets for surveillance. |
| Botnet | A network of compromised computers controlled remotely. |
| Cyber-espionage | Covert surveillance of computer systems for intelligence. |
| Malware | Software designed to harm or exploit computer systems. |
Perspectives and Future Technologies Related to GhostNet
As technology advances, GhostNet and similar cyber-espionage networks will likely become more sophisticated and challenging to detect. Artificial intelligence and machine learning are expected to be integrated into such networks to improve evasion techniques and decision-making processes.
Future technologies may include more advanced encryption methods for covert communications and better methods for evading detection by security systems. As a result, cybersecurity experts will need to stay vigilant and adapt to these evolving threats to safeguard individuals and organizations.
GhostNet and Proxy Servers
Proxy servers can play a significant role in GhostNet operations. Attackers often use proxy servers to mask their true locations and identities, making it difficult for security analysts to trace back the source of attacks. Moreover, attackers can use proxy servers to relay communications between their command centers and the compromised systems in the GhostNet botnet, further obfuscating their activities.
Proxy server providers like OneProxy need to ensure strict security measures to prevent their services from being exploited by malicious actors. Implementing robust monitoring, logging, and authentication mechanisms can help identify and block suspicious activities originating from their servers.
Related Links
For more information about GhostNet and cyber-espionage networks, you can refer to the following resources:
- Tracking GhostNet: Investigating a Cyber Espionage Network – The original report that exposed GhostNet’s operations.
- Cyber Espionage: The GhostNet Ghost in the Machine – A comprehensive analysis of GhostNet’s methods and targets.
- Understanding Botnets: How They Work and How to Defend Against Them – Insights into botnets and their impact on cybersecurity.
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework – Guidelines for improving organizational cybersecurity practices.
Remember, staying informed and vigilant is crucial in the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats and espionage networks like GhostNet.




