Data governance framework is a structured approach that enables organizations to establish policies, processes, and controls to ensure the effective management and use of data across the enterprise. In this article, we will delve into the history, workings, features, types, and future prospects of data governance framework, with a particular focus on its relevance to the proxy server provider, OneProxy.
The Origins of Data Governance Framework
The concept of data governance framework can be traced back to the late 20th century when data management challenges began to emerge with the rapid growth of data volumes and the need for greater data integrity and privacy. The earliest mention of data governance framework can be found in academic papers and government documents in the early 1990s. Initially, data governance was confined to regulatory compliance, but it soon evolved into a comprehensive framework encompassing data quality, security, and data lifecycle management.
Understanding the Data Governance Framework
Data governance framework is a multi-faceted approach that involves people, processes, and technology working together to ensure data consistency, accuracy, and protection throughout its lifecycle. The key objectives of a data governance framework are:
- Data Integrity: Ensuring that data is accurate, reliable, and consistent across the organization.
- Data Security: Implementing measures to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access, breaches, or leaks.
- Compliance: Adhering to legal and regulatory requirements related to data management and privacy.
- Data Lifecycle Management: Overseeing data from its creation to deletion or archival, managing its retention and disposal.
The Internal Structure and Functioning of Data Governance Framework
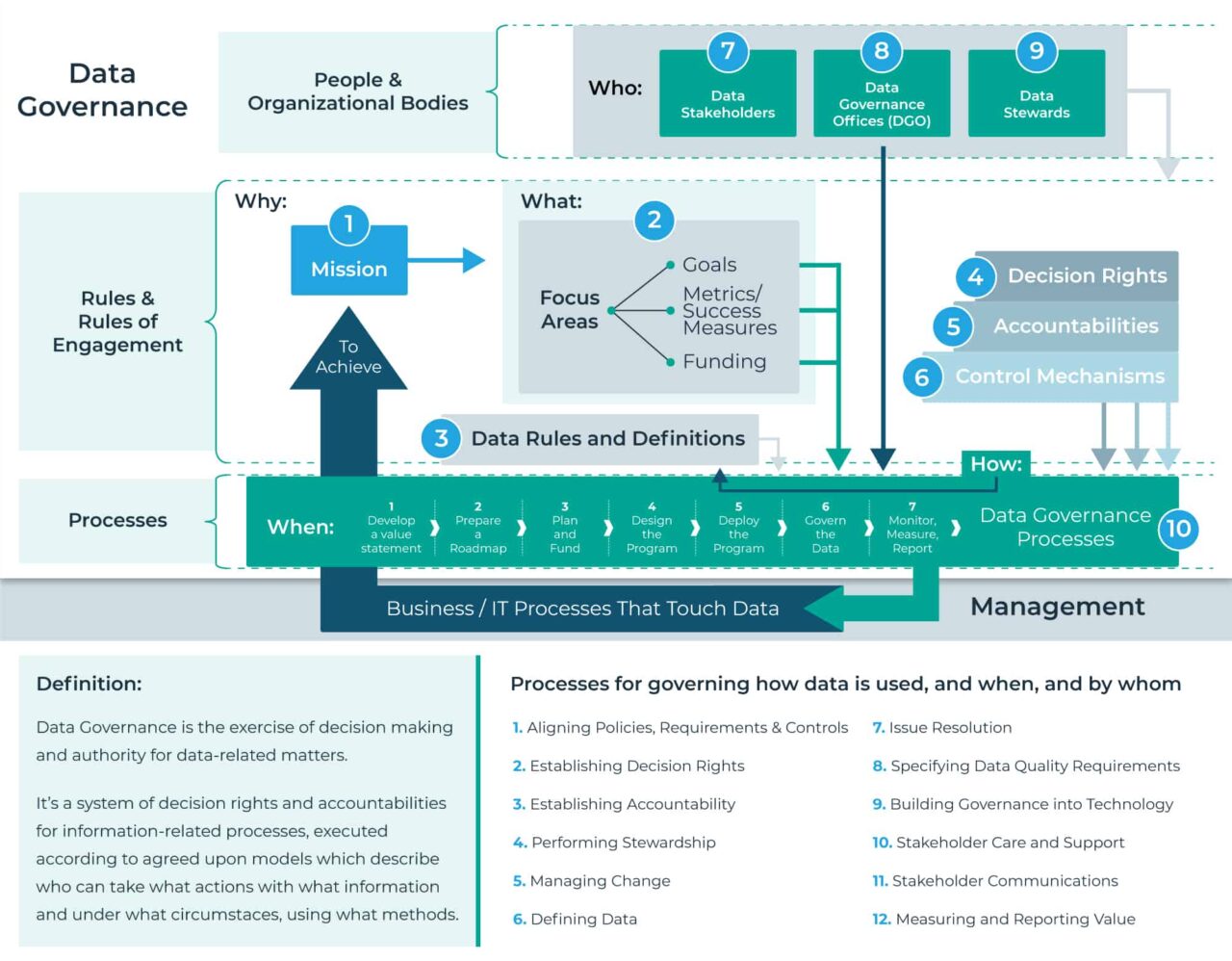
The internal structure of a data governance framework typically consists of the following components:
- Data Governance Board: Responsible for defining data governance policies, procedures, and strategies. Comprises senior executives, data stewards, and subject matter experts.
- Data Stewards: Individuals responsible for data management within specific business units or domains. They enforce data policies and resolve data-related issues.
- Data Management Policies: Set of guidelines and rules governing data quality, access, usage, and privacy.
- Data Quality Tools: Software applications used to monitor, measure, and improve data quality.
- Metadata Repository: Centralized database storing information about data assets, their definitions, and relationships.
- Data Governance Council: Represents business and IT stakeholders, providing input and feedback to the Data Governance Board.
Key Features of Data Governance Framework
The effectiveness of a data governance framework is determined by its key features:
- Accountability: Clearly defined roles and responsibilities for managing data assets and enforcing data policies.
- Transparency: Open communication about data policies, quality metrics, and compliance status across the organization.
- Data Cataloging: Comprehensive inventory of data assets, including their lineage, attributes, and usage.
- Data Standards: Defined guidelines and rules for data naming conventions, formats, and classifications.
- Data Privacy and Security: Measures to protect sensitive data and ensure compliance with data protection regulations.
Types of Data Governance Framework
Data governance frameworks can be categorized based on their focus and scope. Here are three common types:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Centralized | In a centralized framework, data governance is managed by a dedicated team or department. |
| Decentralized | In a decentralized framework, data governance responsibilities are distributed among business units. |
| Hybrid | A hybrid framework combines elements of both centralized and decentralized approaches. |
Using Data Governance Framework and Addressing Challenges
Data governance framework has a wide range of applications across industries. Some common use cases include:
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring compliance with data protection laws, such as GDPR or CCPA.
- Risk Management: Mitigating data-related risks and preventing data breaches.
- Data Quality Improvement: Enhancing data accuracy and reliability.
However, implementing a data governance framework comes with challenges:
- Cultural Change: Encouraging a data-driven culture and gaining buy-in from stakeholders.
- Data Silos: Breaking down data silos to create a unified view of data across the organization.
- Data Ownership: Identifying and assigning data ownership responsibilities.
To address these challenges, organizations should invest in data governance training, adopt data governance best practices, and leverage data governance tools.
Characteristics and Comparison with Related Terms
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Management | Broader term encompassing all aspects of managing data, including storage, access, etc. |
| Data Governance | Focuses specifically on the policies and processes for ensuring data integrity and use. |
| Data Stewardship | Individuals responsible for data management and enforcing data policies. |
Future Perspectives and Technologies
The future of data governance framework lies in advancements in technology, including:
- Artificial Intelligence: AI-driven data governance tools for automated data quality and compliance monitoring.
- Blockchain: Immutable data records and increased transparency through blockchain-based data governance.
- Data Analytics: Leveraging data analytics to identify patterns and trends in data usage and quality.
Proxy Servers and Data Governance Framework
As a proxy server provider, OneProxy can play a crucial role in data governance by ensuring secure and anonymous access to the internet. Proxy servers act as intermediaries between users and web servers, providing an additional layer of privacy and security. By utilizing proxy servers, organizations can enhance data protection, control access to sensitive resources, and monitor internet traffic for potential threats.
Related Links
For more information about data governance framework, you can explore the following resources:
- Data Governance Institute
- Data Management Association International (DAMA)
- Information Governance Initiative (IGI)
Conclusion
Data governance framework is a critical component of modern data management, enabling organizations to ensure data integrity, security, and compliance. By implementing a robust data governance framework, businesses can unlock the full potential of their data, make informed decisions, and gain a competitive edge in the data-driven world. As the volume and complexity of data continue to grow, the role of data governance will only become more crucial, making it an essential practice for businesses of all sizes and industries.




